链表
文章目录
什么是链表
链表是一种用于存储数据集合的数据结构。链表有以下属性:
- 相邻元素之间通过指针连接。
- 最后一个元素的后继指针值为null。
- 在程序执行过程中,链表的长度可以增加或缩小。
- 链表的空间能够按需分配。
- 链表不存在内存空间的浪费(但是链表中的指针需要一些额外的内存开销)。
链表的图示如下:
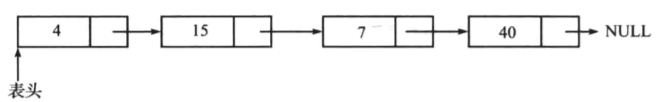
链表与数组比较
链表优缺点
优点:
- 链表不存在内存空间的浪费。
- 链表在执行插入和删除操作有优异的性能。
- 链表的空间能够按需分配。
缺点:
- 不适合随机存取的场景。
- 链表操作需要额外的辅助指针,需要浪费一定空间。
数组优缺点
优点:
- 简单易用。
- 访问元素快(随机访问)。
缺点:
- 大小固定。
- 分配一个连续的存储空间。
- 基于位置的插入操作实现复杂。
单向链表
链表通常指的是单向链表 ,单向链表包含多个节点,每个节点有一个指向其后继节点的next指针。链表中的最后一个节点的next指针为null,表示链表的结束。单链表图示如下:

链表的基本操作
- 遍历链表。
- 在链表中插入一个元素。
- 从链表中删除一个元素。
链表的遍历
遍历一个链表需要以下步骤:
- 沿指针遍历。
- 遍历时显示节点的内容(或计数)。
- 当next指针的值为null的时候结束遍历。
一个遍历链表的函数例子如下:
//遍历带头结点的链表
int getLinkedListLength(Node headNode){
int length=0;
Node current=headNode.next;
while(current!=null){
length++;
current=current.getNext();
}
}
时间复杂度为O(n),用于扫描长度为n的链表。空间复杂度为O(1),仅用于创建临时变量。
单向链表的插入
单向链表的插入操作分为3种情况:
- 在链表的表头插入一个新的节点(链表开始处)。
- 在链表的表尾插入一个新的节点(链表的结尾处)。
- 在链表的中间插入一个新的节点(随机位置)。
链表开始处
操作如下:
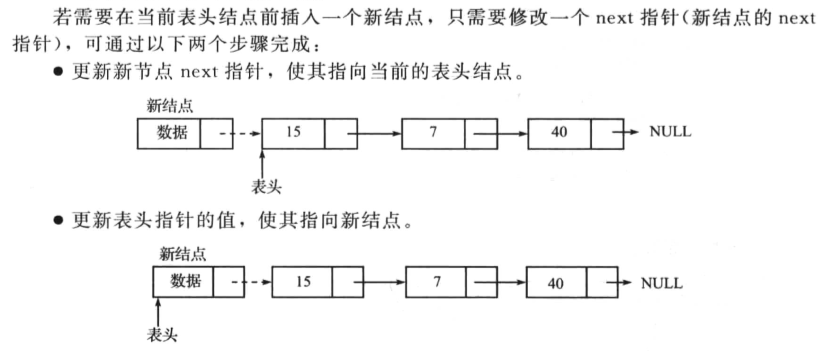
链表的结尾处
操作如下:
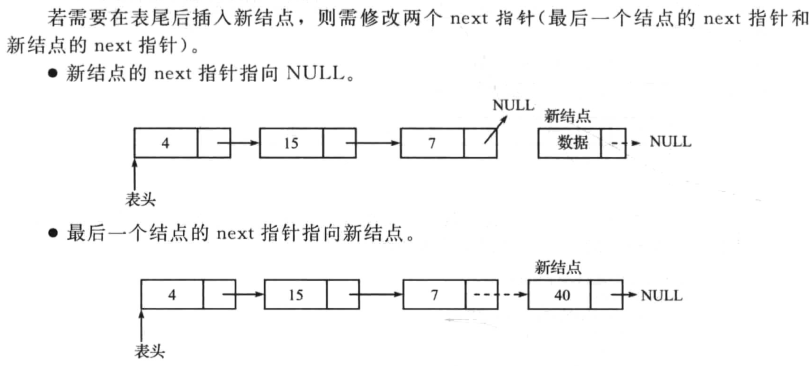
Notice :不要忘记使新插入节点的next指向null。
随机位置
操作如下:
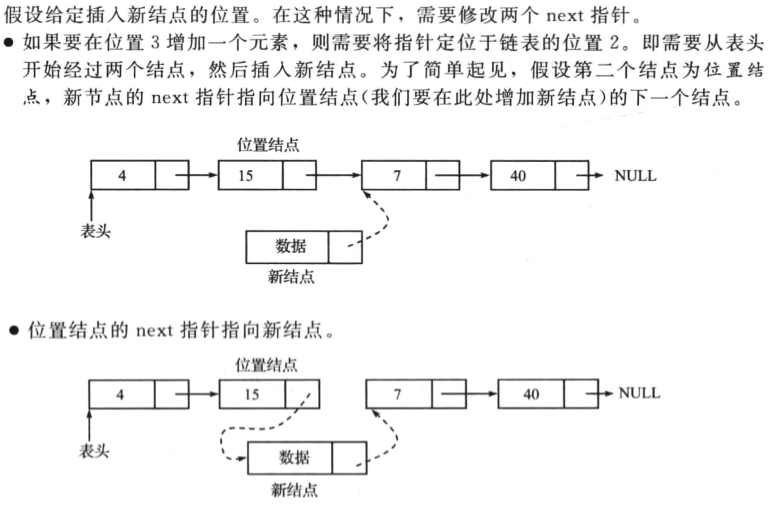
一个实现案例如下(综合插入操作):
//将新节点插入到pos前,且pos是从1开始计算
ListNode insertInLinkedList(ListNode headNode,ListNode nodeToInsert,int pos){
if(headNode==null){//如果链表为空
return nodeToInsert;
}
int size=getLinkedListLength(headNode);
if(pos>size+1||pos<1){//如果插入的位置不对
System.out.println("输入错误,请检查你的插入位置!");
return headNode;
}
if(pos==1){//如果将节点插入到链表的头
nodeToInsert.setNext(headNode);
return nodeToInsert;
}else{//在链表的中间或者末尾插入
ListNode preNode=headNode;
int count=1;
//先找到需要插入的位置
while(count<pos-1){
preNode=preNode.getNext();
count++;
}
//开始插入
ListNode temp=preNode.getNext();
nodeToInsert.setNext(temp);
preNode.setNext(nodeToInsert);
}
return headNode;
}
时间复杂度为O(n)。因为最差的情况下,可能需要在链尾插入节点。空间复杂度为O(1),仅用于创建一个临时变量。
单向链表的删除
与单向链表的插入相似,删除也分为3种情况:
- 删除链表的表头(第一个)节点。
- 删除链表的表尾(最后一个)节点。
- 删除链表中间的节点。
删除单向链表的第一个节点
操作如下:
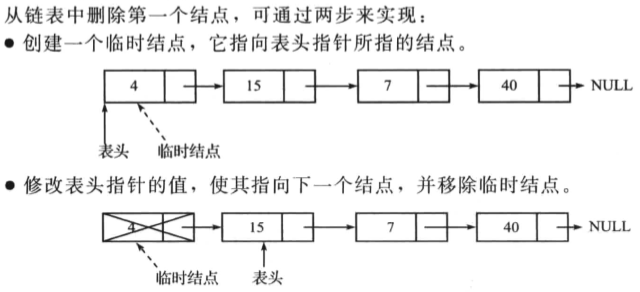
删除单向链表的最后一个节点
操作如下:
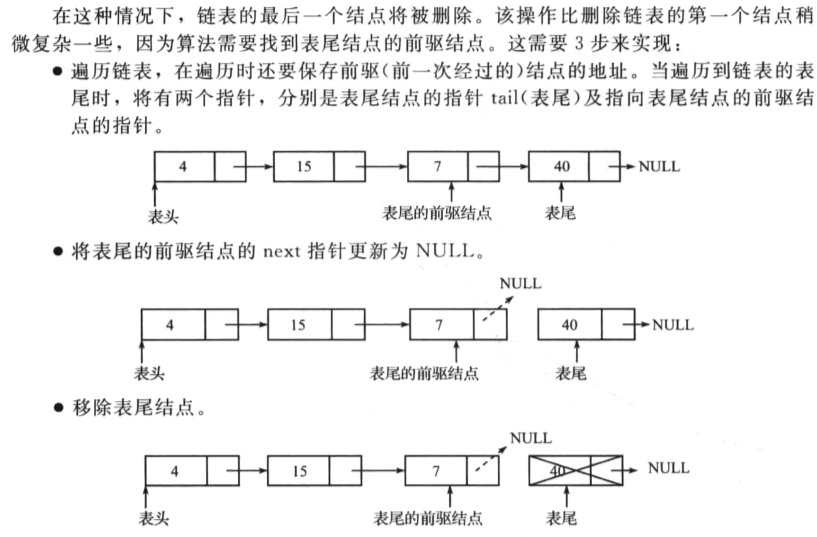
删除单向链表中间的一个节点
操作如下:
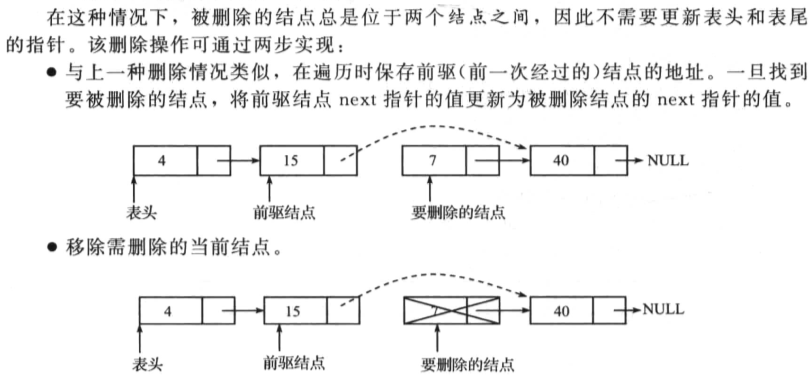
一个代码实现例子如下(综合删除操作):
//删除pos位置的节点
ListNode deleteNodeFromLinkedList(ListNode headNode,int pos){
int size=getLinkedListLength(headNode);
if(pos>size||pos<1){
System.out.println("输出非法,请检查pos的输入!");
return headNode;
}
if(pos==1){//如果删除第一个节点
headNode=headNode.getNext();
return headNode;
}else{//删除中间的节点或者链尾的节点
ListNode temp=headNode;
int index=1;//例子中的索引从1开始
while(index<pos-1){//找到pos位置的前驱节点
temp=temp.getNext();
index++;
}
ListNode deleted=temp.getNext();
temp.setNext(deleted.getNext());
deleted.setNext(null);
deleted=null;//通知JVM回收垃圾
}
return headNode;
}
时间复杂度为O(n),因为最差的情况下,可能需要删除链尾节点。空间复杂度为O(1),因为仅创建了一个临时变量。
删除单向链表
删除单向链表,需要将当前节点存储在一个临时变量里,然后释放当前节点(使当前节点的变量等于null,Java垃圾回收机制会自动回收空间)。当释放当前节点,移动到下一个节点并将其存储到临时变量,然后不断重复该过程直到释放所有节点。一个代码示例如下:
void deleteLinkedList(ListNode headNode){
ListNode current=headNode,next;
while(current!=null){
next=current.getNext();
current.setNext(null);
current=next;
}
}
双向链表
双向链表优缺点
优点:
- 对于链表中给定的一个节点,可以从两个方向进行操作。
- 删除一个节点时候,无需此节点的前驱节点也能删除该节点。
缺点:
- 每个节点需要添加一个额外的指针,因此需要更多的空间开销。
- 每个节点的插入和删除更加费时(需要更多的指针操作)。
双向链表的插入操作
双向链表的插入与单链表一样,分为三种情况:
- 在链表的开头插入一个新节点。
- 在链表的末尾插入一个新的节点。(插入链表的最后)
- 在链表的中间插入一个新的节点。
在双向链表的开始插入一个节点
操作如下:
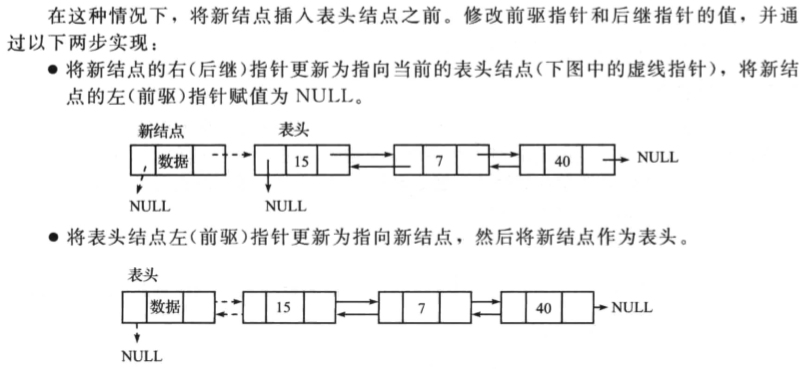
在双向链表的末尾插入一个节点
操作如下:
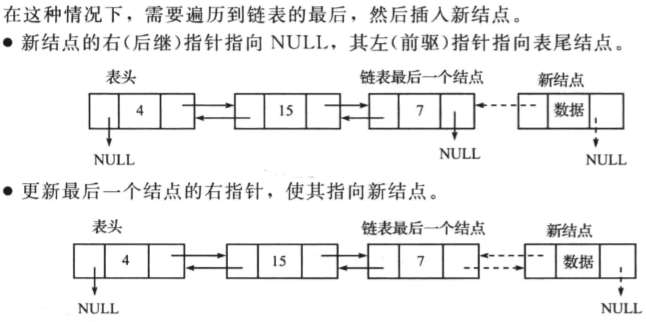
在双向链表的中间插入一个节点
操作如下:
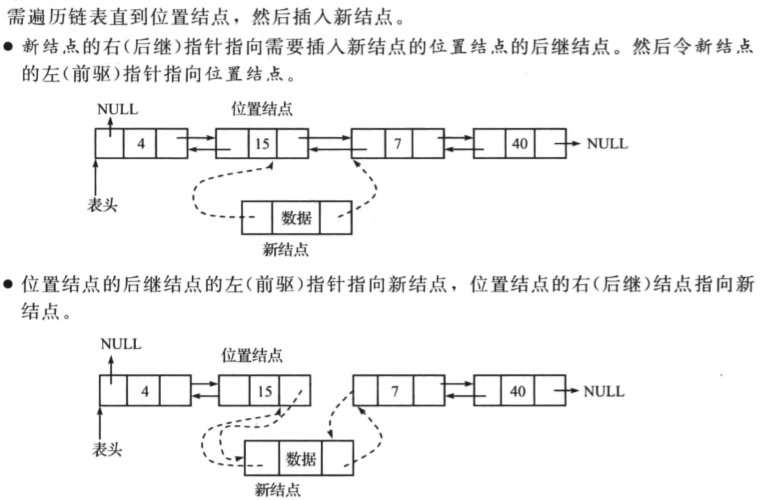
一个代码实现案例如下:
//将新节点插入到pos位置之前
ListNode insertInLinkedList(ListNode headNode,ListNode nodeToInsert,int pos){
if(headNode==null){
return nodeToInsert;
}
int size=getLinkedListLength(headNode);
if(pos>size+1||pos<1){
System.out.println("输入错误,请检查!");
return nodeToInsert;
}
if(pos==1){
nodeToInsert.setNext(headNode);
headNode.setPre(nodeToInsert);
return nodeToInsert;
}else{
ListNode current=headNode;
int count=1;
while(count<pos-1){
current=current.getNext();
count++;
}
ListNode next=current.getNext();
if(next!=null) next.setPre(nodeToInsert);
nodeToInsert.setNext(next);
nodeToInsert.setPre(current);
current.setNext(nodeToInsert);
}
return headNode;
}
时间复杂度为O(n),因为在最差的情况下,需要在链表的尾部进行插入节点。空间复杂度为O(1),用于创建一个临时变量。
双向链表的删除操作
与单向链表的删除相似,也有3种情况:
- 删除链表的表头节点。
- 删除链表的表尾(最后一个)节点。
- 删除链表中间的一个节点。
删除双向链表的第一个节点
操作如下:
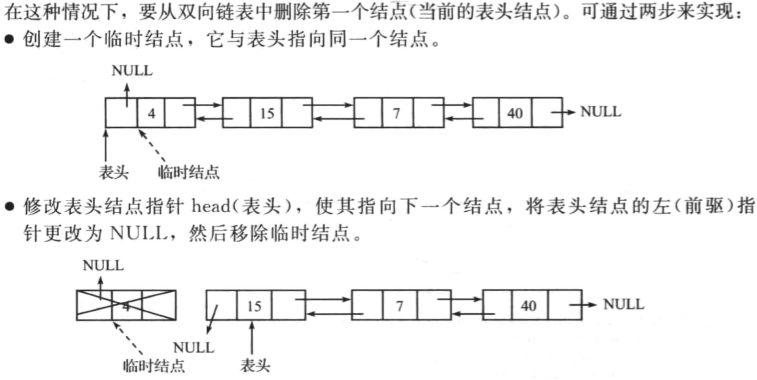
删除双向链表的最后一个节点
操作如下:
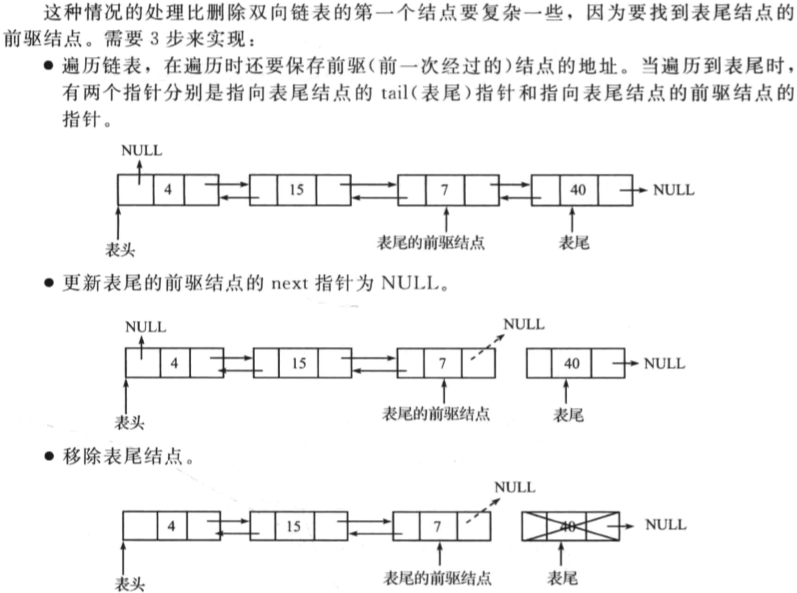
删除双向链表中间的一个节点
操作如下:
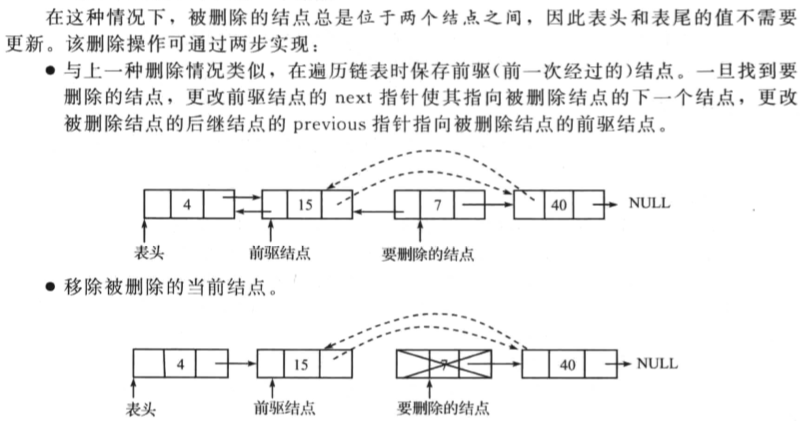
一个代码示例如下:
//删除pos位置的节点,pos从1开始
ListNode delete(ListNode headNode,int pos){
int size=getLinkedListLength(headNode);
if(pos>size+1||pos<1){
System.out.println("输入错误,请检查!");
}
if(pos==1){
ListNode next=headNode.getNext();
headNode.setNext(null);
next.setPre(null);
headNode=next;
return headNode;
}else{
ListNode current=headNode;
int count=1;
while(count<pos){
current=current.getNext();
count++;
}
ListNode next=current.getNext();
if(next!=null) next.setPre(current.getPre());
current.setNext(null);
current.getPre().setNext(next);
current.setPre(null);
current=null;//没有引用指向这个对象,JVM会自动回收此垃圾
}
return headNode;
}
时间复杂度为O(n),因为最差的情况下,可能需要删除链表的表尾节点。空间复杂度为O(1),仅用于创建一个临时变量。
循环链表
循环链表没有结束标志,单项链表和双向链表都采用了一个next指针指向为null来表示链表的结束,但是循环链表没有next指针为null的节点。
统计循环链表的节点的个数
操作如下:
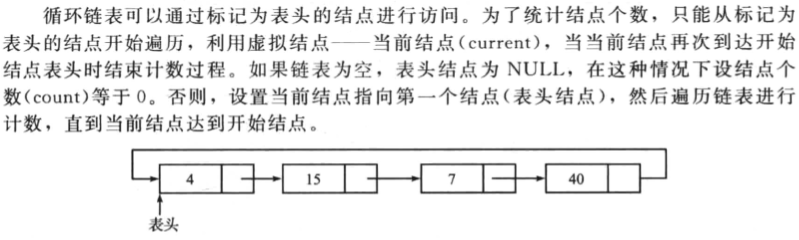
一个代码示例如下:
int getCircularLinkedListLength(CircularLinkedList headNode){
int length=0;
CircularLinkedList current=headNode;
int length=0;
while(current!=null){
length++;
current=current.getNext();
if(current==headNode) break;
}
return length;
}
时间复杂度为O(n),用于扫描长度为n的链表。空间复杂度为O(1),仅用于创建一个临时变量。
输出循环链表的内容
和遍历操作差不多,一个代码示例如下:
void printCircularLinkedListData(CircularLinkedList headNode){
CircularLinkedList current=headNode;
while(current!=null){
System.out.println("数据为:"+current.getData());
current=current.getNext();
if(current==head) break;
}
}
时间复杂度为O(n),用于扫描大小为n的链表。空间复杂度为O(1),仅用于创建一个临时变量。
循环链表的插入操作
循环链表的在中间位置插入节点和单向链表一致,此处只讨论在表头和表尾插入节点的情况。
在循环链表的表尾插入节点
操作如下:
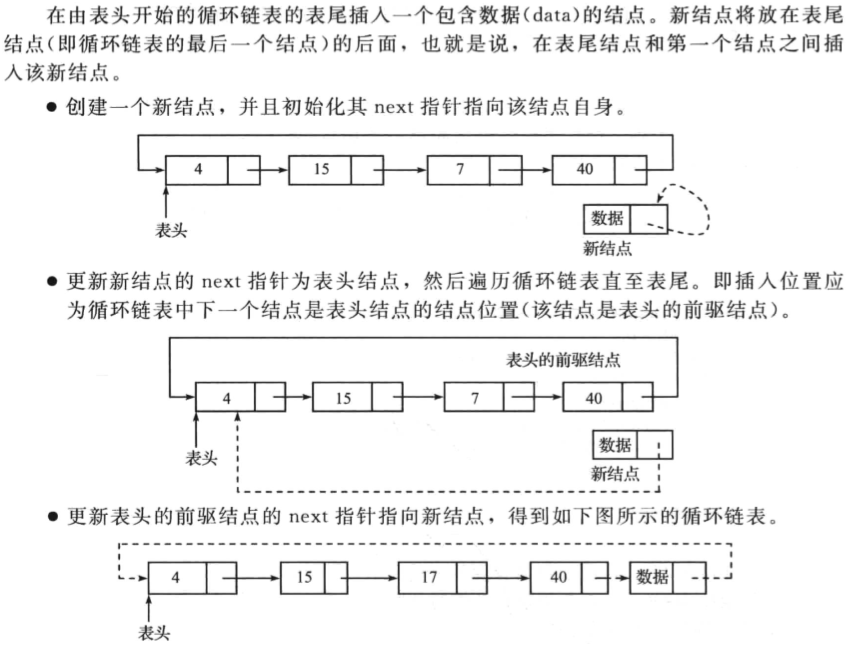
一个示例代码如下:
void insertAtEndInCircularLinkedList(CircularLinkedList headNode,CircularLinkedList nodeToInsert){
nodeToInsert.setNext(nodeToInsert);
if(heaNode==null){
headNode=nodeToInsert;
return headNode;
}else{
//变量到最后一个节点
CircularLinkedList current=headNode;
while(true){
current=current.getNext();
if(current==headNode) break;
}
nodeToInsert.setNext(headNode);
current.setNext(nodeToInsert);
}
}
在循环链表的表头插入节点
操作如下:
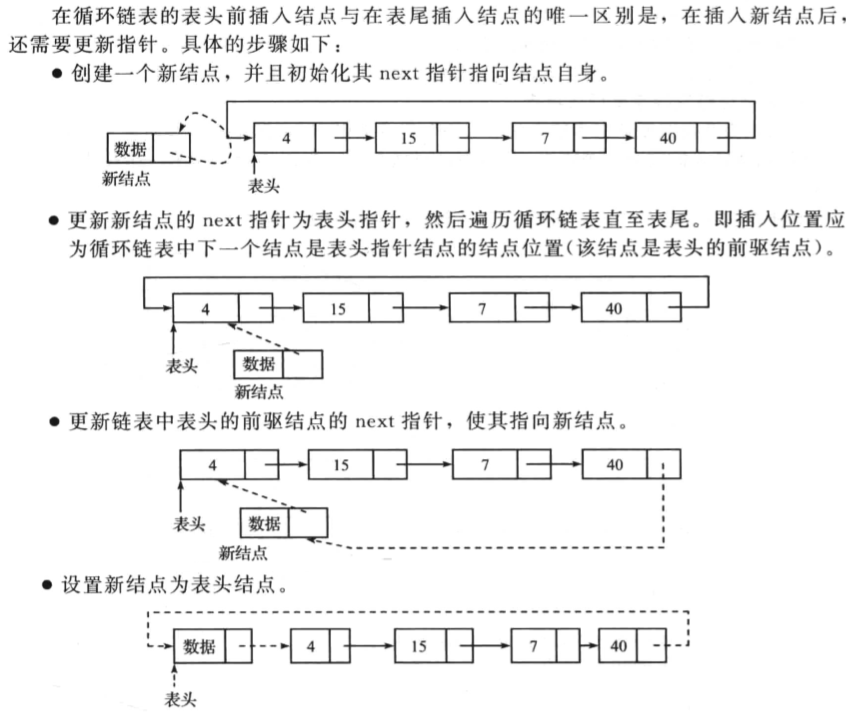
一个示例代码如下:
void insertBeginInCircularLinkedList(CircularLinkedList headNode,CircularLinkedList nodeToInsert){
nodeToInsert.setNext(nodeToInsert);
if(headNode==null){
headNode=nodeToInsert;
return headNode;
}else{
CircularLinkedList current=headNode;
while(true){
current=current.getNext();
if(current==head) break;
}
nodeToInsert.setNext(headNode);
current.setNext(nodeToInsert);
headNode=nodeToInsert;
}
return headNode;
}
循环链表的删除操作
只讨论循环链表的删除表头和表尾的情况。
删除循环链表中的最后一个节点
操作如下:
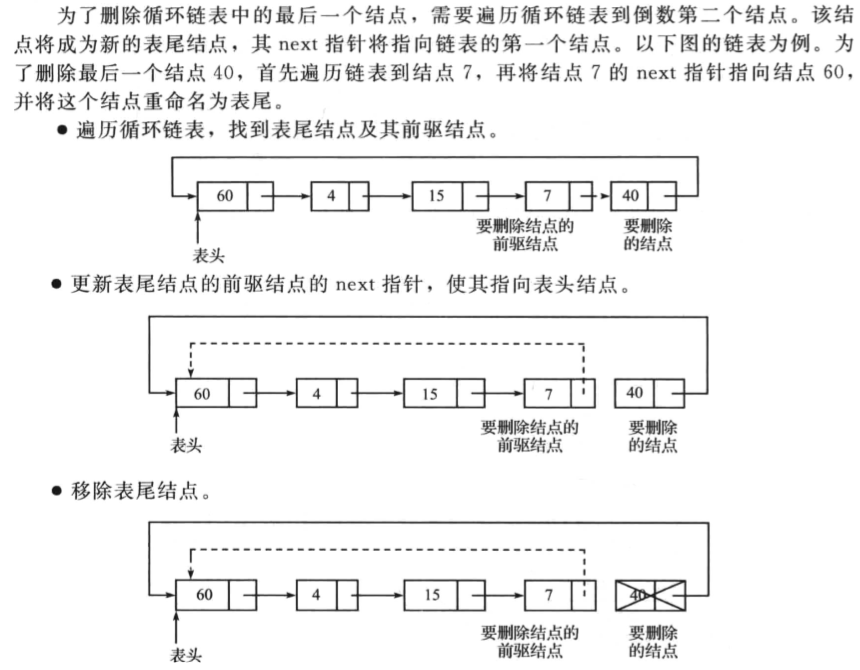
一个代码示例如下:
void deleteLastNodeFromCircularLinkedList(CircularLinkedList headNode){
//先找到倒数第二个节点
CircularLinkedList current=head;
CircularLinkedList temp=head;
if(current==null){
System.out.println("LinkedList is Empty~");
return;
}
while(current.getNext()!=headNode){
temp=current;//保存前一个节点
current=current.getNext();
}
current.setNext(null);
current=null;
temp.setNext(headNode);
}
删除循环链表中的第一个节点
操作如下:
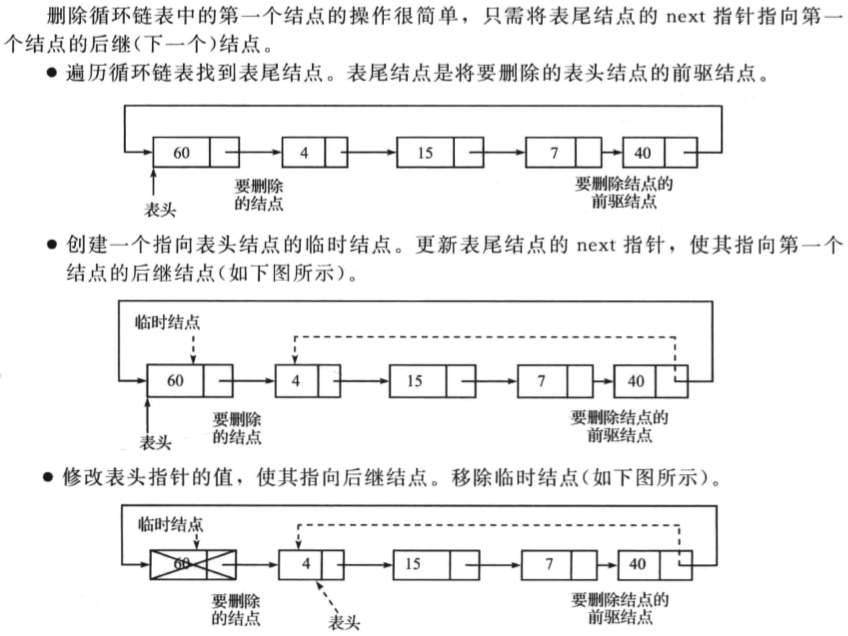
一个代码示例如下:
void deleteFrontNodeFromCircularLinkedList(CircularLinkedList headNode){
CircularLinkedList current=headNode;
if(headNode==null) return;
while(current.getNext!=headNode){
current=current.getNext();
}
current.setNext(headNode.getNext());
CircularLinkedList temp=headNode;
headNode=headNode.getNext();
temp.setNext(null);
temp=null;
}
文章作者 P1n93r
上次更新 2020-03-02
